Spark V10.6 release: New docking functionality and improved search methods for refined molecule design
Spark™ V10.6, the new version of our scaffold hopping and bioisostere replacement tool, enables medicinal and computational chemists to generate innovative ideas for their drug discovery projects with new and improved search methods.
Highlights
-
New ‘docking’ feature, enabling Spark to find fragments picking ligand-protein interactions directly from the protein active site
-
New and improved calculation methods, with significantly improved performance on finding interesting bioisosteres
-
Improved advanced search options, to facilitate the definition of appropriate size criteria during the search
Docking in Spark
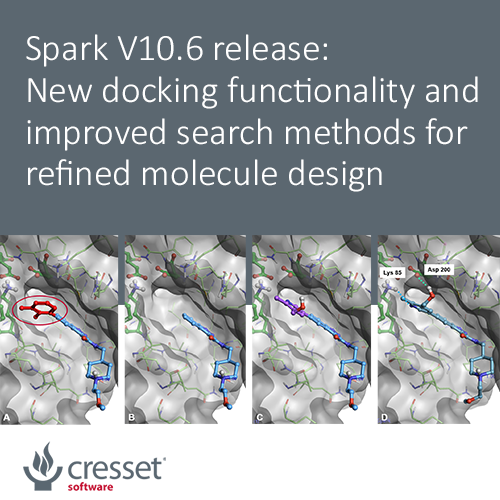
The new ‘docking’ feature enables Spark to find fragments picking ligand-protein interactions directly from the protein active site. Use this method to grow ligands and fragments into unoccupied pockets of the target protein, and whenever you wish to find novel results making interactions with the active site of your protein not mapped by an existing starter or reference molecule.
Spark starts by removing the portion of the starter molecules which you wish to replace. A new fragment is then attached to the truncated starter molecule and placed in the active site of the protein in a sensible orientation guided by the protein electrostatics calculated with the Cresset XED force field. The pose of the new result molecule is then optimized by using the Lead Finder™ ‘score only’ docking mode. Finally, the best results are prioritized by means of the Lead Finder ‘Rank’ scoring function, optimized to correctly reproduce the crystallographic pose of known ligands.
Docking constraints mapping relevant ligand-protein interactions can be easily set to ensure that these are maintained in the result molecules.
Docking in Spark is available as an add-on to traditional Spark bioisostere replacement methods. Customers can contact us to get this add-on.
New and improved calculation methods
Improvements to the ‘traditional’ Spark methods, based on ligand field/shape similarity, include:
-
Higher number of fragments passed to the final stages of scoring
-
New ‘Very Accurate but Slow’ method using shape similarity scoring also in the initial stages of the search
-
Searches starting from a protein-ligand complex using the protein as an excluded volume more efficiently
These improvements increase the accuracy of the Spark search on finding interesting bioisosteres. For example, in a scaffold hopping experiment from the X-ray structure of a mineralocorticoid receptor modulator (PDB 5MWP), Spark finds structures which closely resemble other known mineralocorticoid ligands. The results list also shows a modest enrichment in alternative replacements with high Bioisostere Factor. However, in other cases, these improvements can lead to the identification of up to 30% more results with promising BIF% in typical R-group replacement experiments.
Improved advanced search options
Applying appropriate filters during the search is a great way to reduce the search space for your Spark run, reduce the calculation time, and focus the experiment on the results you really want. This is particularly useful in fragment growing experiments, or when using the docking method, where you want your molecule to grow – but within limits.
To help you with this, the Size Criteria panel of the advanced Spark search options has been improved. This now reports the number of heavy atoms, MW and number of rotatable bonds for both fragments and result molecules. Use this panel in combination with the information in the Starter window and the Advanced Filters to set the ideal physico-chemical profile for the result molecules from your Spark experiment.
Other improvements
This Spark V10.6 release also delivers new science together with significant improvements to the user interface, including:
-
All-new fragment databases, with a total of more than 6.9 million fragments to search
-
Enhanced 2D pictures in all the result tables
-
Ability to distinguish between the different attachment points in the results from scaffold hopping experiments
-
Database generation functionality, including a new reductive amination reagent pattern and new options for the conformation hunt
-
Clearer database information in the search and database updater windows
-
Faster database download
-
Pre-defined filters for common chemical groups and functionality such as Ring, Aromatic Ring, Chiral atom, H-bond donor/acceptor
-
Import/Export of filters, customized calculation methods and radial plot properties
Try Spark on your projects
Current Spark customers will already be in receipt of an email from us with details on how to update to Spark V10.6.
If you’re currently not using Spark, but would like to try it on your project, request an evaluation.





















